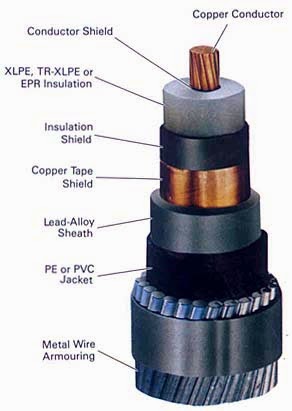
How to change direction of three phase motor in Starters and VFD??
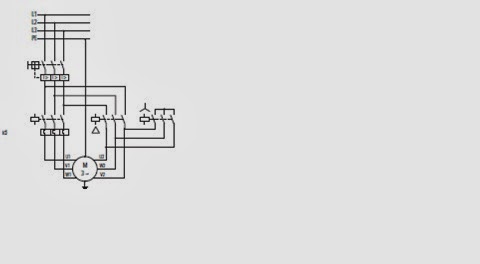
There are some applications where phase sequence required to be changed in 3-Phase motors. Mostly plants which don’t have their own power supply and take from Power Distribution companies phase sequence might change. That Phase sequence can be easily changed in 3-Phase Induction motors by changing two phases from Input Source supply. In Case of Star-Delta Starters 6 no. leads enter into motor so in that case Phase sequence can be changed by changing 2 no. of phases in each pair of 3-Phases. Star-Delta Starter Phase Sequence changed in Star-Delta Starter:- In Case of DOL Soft-Starters Phase sequence can be changed by changing phases in Mains Supply. Is there is requirement of changing Phase sequence in VFD’S???? Answer for the same in that there is no need of changing phase sequence. In Case of VFD there is no need of changing phase sequence as in that case 3-Phase supply is converted into DC supply thereafter that can be converted into AC supply again so